
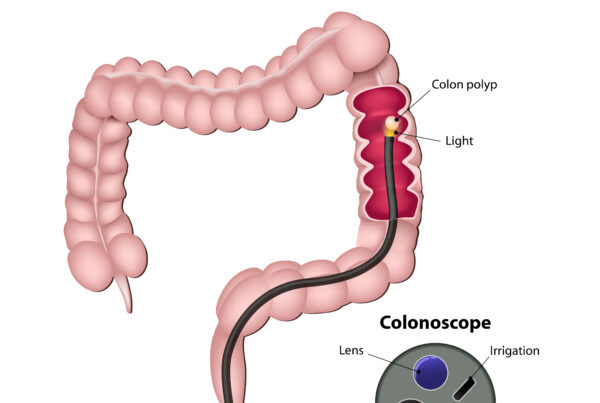
Featured press release: DHPA Supports USPSTF Recommendations to Begin CRC Screening at 45, Calls for More Research on Disparities in Communities of Color
November 13, 2020
Featured press release: DHPA Supports USPSTF Recommendations to Begin CRC Screening at 45, Calls for More Research on Disparities in Communities of Color
The Digestive Health Physicians Association recently announced its support for the U.S. Preventive Services Task…










Recent Comments